- Home
- About
-
Hair
Hair Conditions
- Hair Loss Treatment
- Hair Loss in Men
- Hair Loss in Women
- Male Pattern Baldness
- Female Pattern Baldness
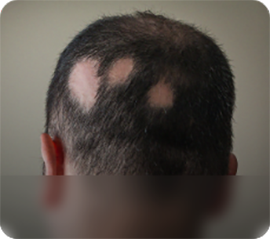
- Alopecia Areata
- Scarring Alopecia
- Androgenetic Alopecia
- Traction Alopecia
Hair Transplantation
- Hair Transplant in Delhi
- Long Hair Transplant
- B.E.S.T. FUE - Patent Method
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)
- Bio Stimulated FUE
- Scalp Micro Pigmentation
- Body Hair Transplant (BHT)
- Eyebrow Transplantation
- Female Hair Transplant
- Beard Transplantation
- Moustache Transplantation
- Failed Hair Transplant Repair
- Artificial Hair Fibers
- Facial Hair Transplant
- Hairline Reconstruction
- Burn Hair Transplant
- Scar Hair Transplant
- Afro Hair Transplant
- FUE Grey Hair Removal
- Microblading
Hair Regeneration Treatment
- SVF
- AMT - Gcell
- Exosomes Therapy
- Stemcell Therapy
- GFC
- LLLT
- Meso Therapy
-
Skin
Skin Concerns
- Dermatology
- Acne Vulgaris
- Allergy
- Dermatitis
- Eczema
- Fungal Infections
- Ingrown Toenails
- Lichen Planus Pigmentosus (LLP)
- Psoriasis
- Urticaria
- Vitiligo
- PCOD
- Xanthelasma
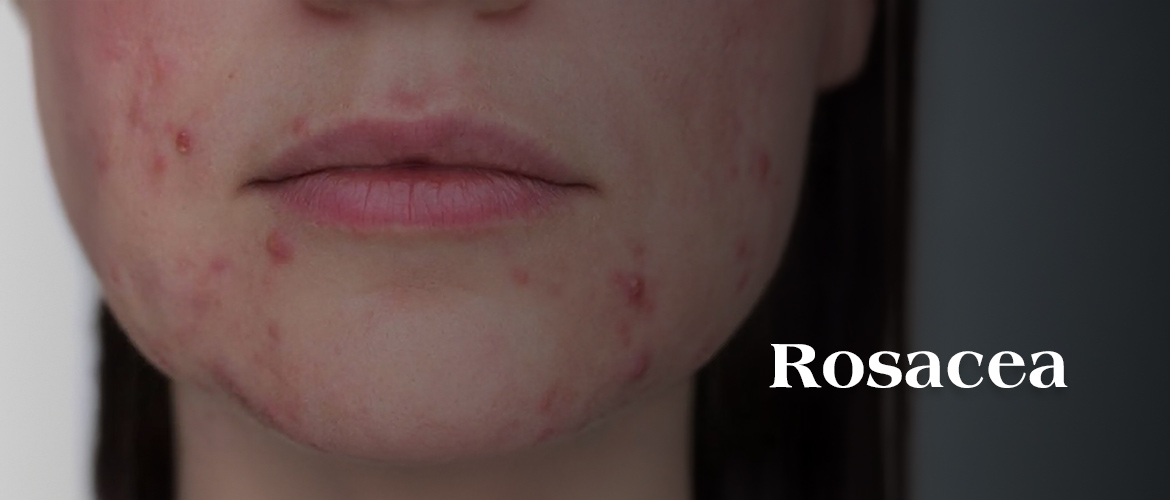
- Rosacea
- Telogen Effluvium
- Acne Scars
- Skin Infections
- Hirsutism
- Leg Veins Treatment
- Melasma
- Open Pores
- Wart
- Eye Bag Correction
- Acanthosis Nigricans
Ageing Treatment
- HIFU
- Neck Lines
- RF Skin Tightening
- Smile Lines
- Sagging Skin
- Thread Lift
- Age Erase
- Instalift Therapy
- Thermi Smooth
- Vampire Facial
- Double Chin Treatment
- Double Chin Reduction Therapy
- Vampire Face Lift
- Thermi Tight
- Morpheus 8
- Fillers
- Exosomes Skin Therapy
Under Eye Treatment
- Dark Circles Removal
- Under Eye Rejuve Peel
- Under Eye Fillers
- Under Eye Boosters
- Tear Trough Correction
- Instagow Therapy for Under Eye
Pigmentation Treatment
- Freckles
- Depigmentation Peels
- Skin Burn/Sun Burn
- Cosmelan
- Glow Peel
- Dermapen 4 for Pigmentation
- Dermapen for Glow and Hydration
- Vampire Facial
- Profhillo
- Hydra Facial Basic
- Hydra Facial Elite
- Skin Boosters
- Face GFC Therapy
Skin and Care
- Femilift
- Liposuction
- Ear, Nose Piercing
- Skin Treatment
- Skin Whitening Treatment
- Dark Circle Treatment
- Plastic Surgery Delhi
- Body Sculping/Shaping
- Skin, Hair & Nail Diseases Hymenoplasty/Labiasty
- Breat Reduction and Augmentation
Anti Ageing
- Fillers
- Wrinkles
- CO2
- Anti Wrinkle Agent
- Anti Wrinkle Injections
- Cheek Contour Restoration
- Cheek Fillers
- Forehead Wrinkles and Lines
- Lip Fillers
- Lip Rejuve Peel
- Lip Pixel
- Lip Boosters
- Instaglow Therapy for Lips
- Chemical Peel
- Injectables
- Microdermabrasion
- RF Skin Tightening
- I.V. Treatment
- Botox
- Skin Boosters
- Derma Roller (Microneedling)
Thermi Technology
Laser and Lights
- Photo Facial
- Scar Treatment
- Stretch Marks Treatment
- Harmony XL with SHR
- Diode Lase with SHR (SOPRANO)
- Laser Hair Reduction
- Laser Resurfacing
- Laser Hair Reduction for Females
- Laser Hair Reduction for Males
- Laser Hair Reduction for Unwanted Hair Growth
- Laser Hair Reduction for Arms
- Laser Hair Reduction for Legs
- Full Body Hair Removal
- Face Laser Hair Reduction
- Laser Hair Reduction for Underarms
- Skin Laser Hair Reduction
- Birthmark Laser Removal
- Tattoo Removal
- Male Laser Removal
- Warts Laser Removal
- Bikini Laser Hair Reduction
Scar Treatment
- Burn Scars
- Chicken Pox Scars
- Dermapen 4 Treatment
- Stretch Marks
- Acne and Acne Scars
- Dermafrac
Acne Treatment
- Acne Peels
- Advanced Acne Treatment
- Carbon Peels
- Chemical Peels
- Fractional Laser
- Subscision
- Radiofrequency Microneedling
- Excimer for Vitiligo
- Cautery for Molluscum
- Acne Clean Up Facial
- Lasers for Freckles
- Microneedling Radiofrequency for Stretch Marks
- Microneedling Radiofrequency with Boosters for Stretch Marks
MediFacial
- Oxy Facial
- Oxyglow
- Red Carpet Peel
- Party Facials
- Halloween MediFacial
- InstaBright Rejuvenation
- Powerlift MediFacial
- Power Glow Facial
- IV Infusions for Glow
Skin Treatment
- Acne Scar Surgery
- Cryosurgery
- Cyst Surgery
- Earlobe Repair
- Mole Surgery
- Scar Reduction Surgery
- Skin Biopsy
- Skin Tag
- Vitiligo Surgery
- Corns and Calluses
- Molluscum
- Electrocautery for Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra
- Electrocautery for Tags
- Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra (DPN)
- Laser for Moles
- Cautery for Warts
- Scar Removal
Skin Glow
- Peels
- Laser
- I.V. Treatment
- I.V. Glutathione
- Skin Whiting Treatment
- Microdermabrasion
- Hydra Facial
- Blog
- Offers
- Gallery
- Contact