Female Pattern Baldness (FPB), also referred to as female pattern hair loss (FPHL) or androgenic alopecia, is a common genetic condition characterized by gradual thinning of hair on the scalp. Unlike male paern baldness, FPB has distinct patterns and progression, and its impact varies widely among individuals.


Hair loss often starts with a noticeable widening of the part at the center of the scalp.
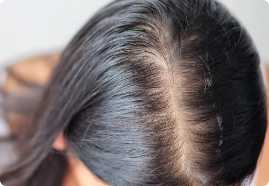
Hair thinning spreads to the top and crown, forming the distinct Christmas tree pattern.

Unlike male pattern baldness, the frontal hairline is typically unaffected.
Female pattern hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a progressive condition that leads to thinning of hair over time. Unlike male pattern baldness, which typically results in a receding hairline or bald patches, female pattern hair loss presents as a general thinning across the scalp, particularly at the crown and parting area. While complete baldness is rare in women, the reduction in hair density can be distressing and impact self-confidence.
The primary cause of female pattern hair loss is a combination of genetic predisposition and hormonal changes. Women who have a family history of hair thinning are more likely to experience this condition. The hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) plays a crucial role in shrinking hair follicles, leading to shorter, finer strands and a decrease in overall hair volume. Although DHT is more commonly associated with male hair loss, women also produce small amounts of this hormone, which can influence hair follicle sensitivity.
One of the earliest signs of female pattern hair loss is a widening of the parting or an overall reduction in hair volume. The condition progresses gradually, and withoutintervention, hair continues to thin, making the scalp more visible. However, unlike other forms of hair loss, female pattern hair loss does not usually result in sudden or excessive shedding. Instead, hair follicles shrink over time, leading to a steady decline in hair density.
While female pattern hair loss is not completely reversible, early diagnosis and treatment can slow down its progression and, in some cases, stimulate regrowth. Medical treatments such as topical minoxidil, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) have shown effectiveness in strengthening existing hair and encouraging regrowth. Additionally, maintaining a healthy scalp environment through proper nutrition, stress management, and gentle hair care practices can help support overall hair health.
Genetics: FPB has a strong hereditary component, with multiple
genes involved. These can be inherited from either or both
parents.
FPB can begin as early as puberty or as late as post-menopause, depending on individual genetics and hormonal changes.
While FPB is not entirely reversible, several treatments can slow its progression and promote regrowth.
Early detection and intervention can significantly slow down hair loss.
Regular consultations with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist ensure that treatments are tailored to individual needs.
Rediscover confidence with solutions
tailored to address female pattern baldness.

The Truth Regarding
Hair Patch

Cheap Hairloss Treatment
A Threat to the Hair and You
PRP Face Facial
Detail you should know
Thing You Need to Know
About Alopecia Areata
Long Hair
Tranplant

How PCOD Affect
Your Skin
Eyebrow
Transplant

Hair Care Mistakes
To Avoid This Winter
Facts About New Hairline
After Restoration

Dyeing Hair with Psoriasis
9 Things to Know First
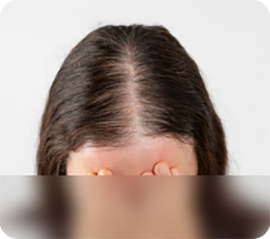
Hair Thinning
Causes and Cure

Can Stress Cause
Hair Loss