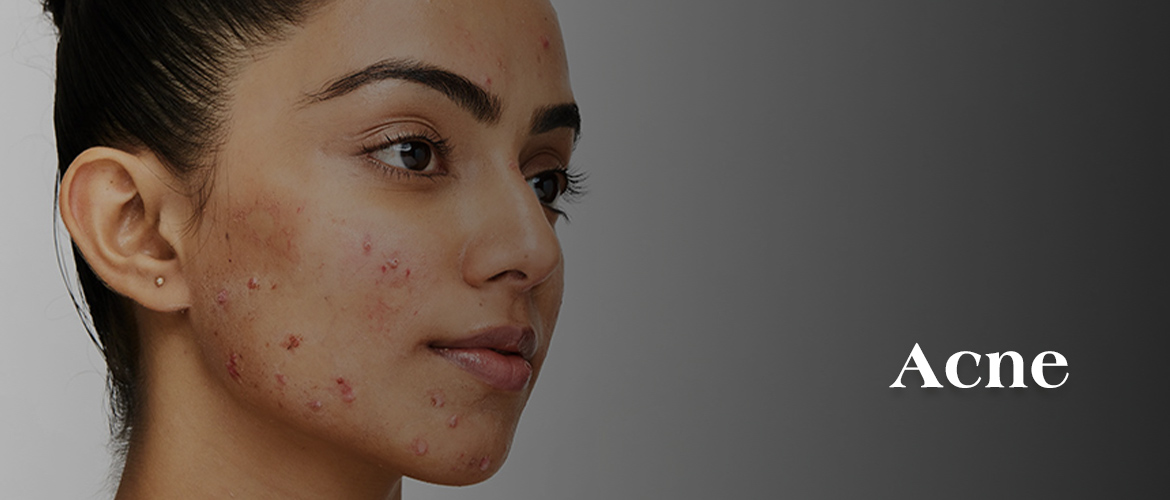
Causes of Acne
Acne develops due to a combination of factors that disrupt the skin's normal function, leading to breakouts and inflammation.
Overproduction
of Sebum (Oil)
Excessive oil production by the sebaceous glands makes the skin more prone to clogged pores and bacterial growth.
Clogged Hair
Follicles
Dead skin cells and oil accumulate in the follicles, forming blockages that lead to the development of blackheads and whiteheads.
Bacterial
Infection
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria thrive in clogged pores, triggering inflammation and pus-filled lesions.
Comedogenic
Skincare Products
Using heavy or pore-clogging makeup, moisturizers, and sunscreens can lead to breakouts by trapping oil and bacteria in the skin.
Stress and Lack
of Sleep
Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that stimulates oil glands, worsening acne. Poor sleep weakens the skin's ability to heal and regulate oil production.
Hormonal
Fluctuations
Changes in hormone levels, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, menstruation, and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), contribute to excessive sebum production.
Treatment for Acne
Managing acne requires a combination of medical treatments, skincare routines, and lifestyle adjustments tailored to the severity and type of acne.
Topical Treatments
Benzoyl Peroxide
Reduces bacteria and helps unclog pores, effective for mild to moderate acne.
Salicylic Acid
Exfoliates the skin, preventing clogged pores and reducing inflammation.
Retinoids
(Tretinoin, Adapalene)
Accelerate cell turnover, preventing new acne and reducing breakouts
Topical Antibiotics
Clindamycin and erythromycin help control bacterial growth and inflammation.
Oral Medications
Antibiotics
Doxycycline and minocycline reduce bacterial infection and inflammation in moderate to severe acne cases.
Hormonal Therapy
Oral contraceptives and spironolactone help regulate hormone levels and oil production in women with hormonal acne.
Isotretinoin (Accutane)
A powerful oral retinoid used for severe cystic acne, reducing sebum production and preventing scarring.
Professional Treatments
Chemical Peels
Reduces bacteria and helps unclog pores, effective for mild to moderate acne.
Laser Therapy
Exfoliates the skin, preventing clogged pores and reducing inflammation.
Extractions
Accelerate cell turnover, preventing new acne and reducing breakouts
Microneedling
Stimulates collagen production, improving acne scars and skin texture.
Lifestyle Changes for Acne Management
Adopting healthy habits can complement medical treatments and prevent frequent breakouts.

Daily Skincare Routine
Wash your face twice a day with a gentle, oil-free cleanser to remove dirt and excess oil without stripping the skin.

Avoid Picking and Touching
Picking at pimples can spread bacteria and lead to scarring and hyperpigmentation.

Use Non-Comedogenic Products
Choose oil-free and non-comedogenic skincare and makeup to prevent clogged pores.

Balanced Diet
Incorporate fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while avoiding processed and sugary foods that can trigger acne.

Hydration and Sleep
Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins and ensure proper skin hydration. Get 7-9 hours of sleep to allow the skin to repair and regenerate.

Stress Management
Engage in activities like yoga, meditation, and regular exercise to reduce stress-related acne flare-ups.